Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Dive into the intricate world of Scope 3 emissions with our comprehensive blog. Uncover the complexities, implications, and strategies for measuring and managing indirect carbon footprints. Stay informed, embrace sustainability, and navigate the path to a greener future

While Scopes 1 and 2 emissions have historically dominated discussions, the silent yet impactful player—Scope 3 emissions—emerges as a critical factor in the sustainability landscape. In an era where the call for environmental responsibility reverberates louder than ever, organizations find themselves at a crossroads, grappling with the complexities of their carbon footprint.
On average, Scope 3 emissions account for a whopping 70 to 90 % of a company’s total carbon footprint. This includes indirect emissions generated throughout the entire value chain, from sourcing raw materials to product disposal.
This blog embarks on a journey into the intricate world of Scope 3 emissions, offering a detailed exploration of their nuanced definition, the profound impact on sustainability goals, categorization spanning the entire value chain, the myriad challenges encountered in measurement, the strategic importance for organizations, their alignment with global reporting initiatives, and the multifaceted benefits that unfold when actively engaging in their reduction.
According to UN, the news appears to be dire for the year 2030, when greenhouse gas emissions will be 10% higher than they were in 2010.
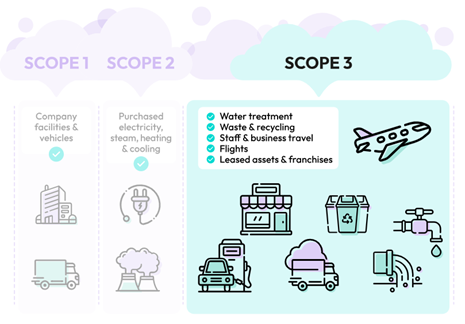
Carbon accounting the bedrock of environmentally responsible business practices, involves the meticulous categorization of emissions into three scopes. While Scope 1 encapsulates direct emissions emanating from owned or controlled sources, and Scope 2 delves into the realm of indirect emissions from purchased energy, Scope 3 transcends organizational boundaries. It encompasses a vast array of indirect emissions intricately interwoven throughout the entire value chain. This comprehensive approach provides organizations with a panoramic view, enabling a holistic understanding of their environmental impact. By understanding and reducing these three scopes of emission, organizations can help reduce their overall carbon footprint and help mitigate climate change.

Over 70 to 90 % of a typical company’s total emissions come from Scope 3, making it a crucial focus for achieving net zero by 2050 and limiting global warming to 1.5°C. Addressing Scope 3 emissions not only aids in the climate transition but also positions companies to manage risks and capitalize on opportunities. Global regulators, including the EU Commission and the US SEC, are pushing for mandatory climate disclosures, emphasizing Scope 3 emissions. Initiatives like the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) set specific criteria for validating Scope 3 reduction targets, reflecting a growing momentum with over 5,600 companies aiming to align with SBTi.
Amidst the pursuit of sustainability, understanding the intrinsic significance of Scope 3 emissions becomes paramount. While Scopes 1 and 2 focus on emissions directly within the operational realm, Scope 3 unravels a broader narrative, shedding light on the environmental repercussions associated with supply chains, product life cycles, and various other indirect sources. The imperative lies in recognizing that addressing Scope 3 emissions is not merely a checkbox for sustainability; it is an integral component in achieving comprehensive sustainability goals and making meaningful contributions to global initiatives combatting climate change.
Upstream (Supply Chain-Related Emissions)
The upstream facet of Scope 3 emissions is a exploration into the environmental impact woven intricately throughout the supply chain. From the extraction and production of raw materials to the transportation of goods, organizations are faced with the challenge of understanding and mitigating emissions at every juncture. As globalization tightens its grip, the need to navigate the complexities of upstream emissions becomes not just a choice but a necessity for sustainable practices.
Downstream (Emissions from Product Use and Disposal)
Downstream emissions usher us into the realm of the product life cycle, where the environmental narrative extends into the hands of consumers. Energy consumption, emissions, and waste generated during the use of products create a downstream ripple effect. Organizations must broaden their perspective to encompass the entire life cycle of a product, addressing its creation, utilization, and ultimate disposal or recycling.
Other Indirect Emissions
Beyond the traditional realms, Scope 3 extends its reach to encompass a myriad of indirect emissions. Business travel, employee commuting, and investments—each contributes to the complex tapestry of an organization’s environmental impact. These emissions, although not directly controlled, remain integral to the overall operation. Recognizing and categorizing these diverse sources provide a more comprehensive and nuanced picture of an organization’s environmental footprint.
Measuring Scope 3 emissions, proves to be a formidable challenge. Unlike the more straightforward Scopes 1 and 2, where emissions are directly under organizational control, Scope 3 introduces a myriad of variables that extend beyond organizational boundaries. The challenges encompass the vast and intricate nature of global supply chains, the dynamic intricacies of product life cycles, and the complexities associated with obtaining accurate information from external stakeholders. Accurate measurement encounters hurdles in the form of incomplete data, varying reporting standards, and the inherent uncertainties associated with predicting downstream emissions over a product’s entire life cycle.
Exploring the Challenges in Measuring Scope 3 Emissions.
Dive into our blog to understand the complexities and solutions in quantifying indirect carbon footprints.
Understanding and addressing Scope 3 emissions is a strategic imperative for organizations committed to responsible business practices.
Scope 3 emissions offer organizations a comprehensive view of their environmental impact. This holistic perspective extends beyond immediate operational control, empowering organizations to develop effective sustainability strategies that encompass the entire value chain.
Organizations proactively engaged in assessing and mitigating their Scope 3 emissions position themselves for strategic decision-making. The insights gained from understanding the intricacies of the entire value chain enable organizations to identify areas for improvement, implement targeted emission reduction measures, and enhance overall sustainability in a strategic and intentional manner.
In an era where stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulatory bodies, demand transparency and accountability, addressing Scope 3 emissions aligns with these heightened expectations. Demonstrating a commitment to transparency in reporting not only meets stakeholder expectations but enhances corporate credibility. It reflects an organization’s commitment to corporate responsibility, extending beyond regulatory requirements to showcase a genuine dedication to responsible business practices.
Why Achieving Net Zero Requires Tackling Scope 3 Emissions.
Explore our blog to understand the critical role of indirect carbon footprints in the journey towards a sustainable and carbon-neutral future.
Know more
Companies should prioritize measuring their Scope 3 emissions for various compelling reasons. Foremost among them is the enhanced transparency it brings to their supply chain, setting an example for other actors in the same chain to report emissions more effectively. This leadership by example fosters a conducive environment for overall improvement. The benefits extend beyond individual businesses to society, creating a positive spillover effect and raising standards. On a broader scale, it enables the economic sector to collectively address the urgency of climate change by tackling indirect carbon emissions collaboratively.

A myriad of global reporting initiatives and frameworks are actively encouraging organizations to disclose their Scope 3 emissions. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), an international independent standards organization, provides a comprehensive framework for sustainability reporting. Parallel frameworks, such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), offer specific guidance on measuring and reporting Scope 3 emissions. Organizations are increasingly not just encouraged but urged to disclose their Scope 3 emissions as part of broader sustainability reporting. This disclosure aligns with international reporting standards and facilitates benchmarking, allowing organizations to compare their performance with industry peers.
Actively working to reduce Scope 3 emissions not only aligns with environmental goals but often leads to tangible financial benefits. The optimization of supply chain processes, the adoption of energy-efficient practices, and the incorporation of sustainable product design contribute not only to environmental sustainability but also to cost savings, positively impacting the organization’s bottom line.
The reduction of Scope 3 emissions becomes a catalyst for enhancing an organization’s reputation and fostering brand loyalty. In an era where consumers are increasingly drawn to businesses prioritizing sustainability and environmental responsibility, a positive reputation as a socially responsible organization not only attracts environmentally conscious consumers but also fosters long-term brand loyalty and customer trust.
Organizations that actively work to reduce Scope 3 emissions position themselves as trailblazers in sustainable practices within their respective industries. This market leadership not only attracts environmentally conscious consumers but also sets a positive example for competitors and peers. It becomes a testament to the organization’s commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices.
Beyond financial and reputational gains, the reduction of Scope 3 emissions holds intrinsic value in contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts. Organizations that address emissions throughout the value chain play a crucial role in the global endeavor to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Actively engaging in emission reduction efforts showcases environmental stewardship, emphasizing a commitment to a healthier planet and setting an example for responsible corporate citizenship.
According to the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), the number of companies setting science-based targets for Scope 3 emissions has increased by 250% since 2019. This surge indicates a growing commitment to tackling the full range of climate impacts.
Technology solutions streamline the measurement of Scope 3 emissions by automating data collection, offering advanced analytics, providing supply chain visibility, and employing innovative technologies like blockchain and IoT. These tools empower companies to make informed decisions, set meaningful emission reduction targets, and contribute to broader sustainability goals.
Technology automates the collection of diverse and complex data sources related to supply chains and business operations. This reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and ensures comprehensive coverage of Scope 3 emissions. Technology solutions provide real-time visibility into supply chain activities, allowing companies to trace the environmental impact of their products and services throughout their life cycle. This visibility is crucial for understanding and managing Scope 3 emissions. Specialized carbon accounting software simplifies the complex task of calculating emissions by offering standardized methodologies. These tools streamline the measurement process and ensure compliance with reporting standards. Some companies leverage blockchain for transparent and tamper-proof documentation of emission data. This ensures the integrity of the reported information and builds trust among stakeholders.
Remote sensing technologies and satellite imagery provide valuable insights into land-use changes, deforestation, and other factors contributing to Scope 3 emissions. This data enhances the precision of emissions calculations. Cloud-based platforms facilitate collaboration among supply chain partners, allowing them to share emission-related data securely. This collaborative approach ensures a more comprehensive understanding of Scope 3 emissions across the entire value chain.
TraceX’s Digital Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) platform significantly contribute to the measurement and management of Scope 3 emissions by offering comprehensive and streamlined solutions:
TraceX provides end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, allowing companies to track their products or commodities from origin to destination. This visibility ensures that all relevant emission sources are identified and measured. The platform enables real-time tracking of key activities, such as production, transportation, and processing, contributing to Scope 3 emissions. This data accuracy and immediacy enhance the precision of emission calculations.
TraceX employs standardized methodologies for data collection and reporting, ensuring consistency and compliance with emission measurement standards. This simplifies the complexity of data reporting and enhances comparability. Leveraging blockchain technology, TraceX ensures the integrity and transparency of emission-related data. This tamper-proof system builds trust among stakeholders and provides a secure foundation for Scope 3 emissions reporting.
The platform allows companies to trace the carbon footprint of their products or commodities, providing a clear understanding of the environmental impact at each stage of the supply chain. This traceability is crucial for managing and optimizing Scope 3 emissions. It supports companies in generating compliance reports for various sustainability standards and initiatives, including Science-Based Targets and regulatory requirements. This ensures that companies meet their reporting obligations accurately.
In conclusion, the journey toward understanding and reducing Scope 3 emissions is a multifaceted endeavor requiring a strategic, holistic, and intentional approach. The intrinsic significance of these emissions, the nuanced categorization of their sources, the persistent challenges in measurement, and active participation in global reporting initiatives are essential steps for organizations committed to sustainability.
The benefits of Scope 3 emission reduction extend far beyond financial gains, encompassing reputational enhancement, market leadership, and a positive environmental impact. As organizations navigate the intricate landscape of carbon accounting, recognizing the transformative power of mitigating Scope 3 emissions positions them as leaders in the global shift toward responsible and sustainable business practices.
In the pursuit of a resilient and sustainable future, organizations that embrace the intricacies of Scope 3 emissions not only mitigate their environmental impact but also contribute to a collective effort for a healthier, more sustainable, and resilient global community.
