Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Uncover the Journey of Sustainable Aviation Fuel: From Feedstock to Fuel - Explore the fascinating narrative behind SAF production, its feedstock sources, and the promising future it holds for greener aviation.
In recent years, a growing interest has emerged in sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) as a crucial component of the aviation industry’s response to climate change and environmental sustainability. As the aviation sector grapples with the pressing need to reduce its carbon emissions, SAFs have come to the forefront as a promising solution.
According to IATA, Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) could contribute around 65% of the reduction in emissions needed by aviation to reach net-zero in 2050.
In this comprehensive blog explores the intricate world of SAFs, shedding light on the entire “feed to fuel” process, and the profound potential they hold in revolutionizing air travel.
Sustainable Aviation Fuels, often referred to as SAFs, constitute a diverse array of alternative fuels aimed at mitigating the aviation industry’s greenhouse gas emissions. These fuels encompass various forms, but the most prevalent SAFs are biofuels, derived from organic materials such as crops, algae, and waste. Additionally, there are synthetic fuels generated from renewable electricity and carbon capture technology.
The environmental significance of SAFs is undeniably profound. When compared to conventional jet fuels, SAFs are capable of reducing carbon emissions by up to 80%. Furthermore, they release fewer harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, resulting in improved air quality and a more ecologically balanced environment.
The production of SAF aims to reduce the carbon footprint of the aviation industry and promote environmental sustainability.
The aviation industry has set ambitious goals to reduce its carbon emissions, with SAFs positioned as a cornerstone of this decarbonization strategy. By 2050, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) has set a goal to reduce net aviation emissions to half of the 2005 levels, and SAFs are considered the most feasible solution to achieve this ambitious target.
Recently, the Indian Institute of Petroleum (IIP), a laboratory operating under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), has formed partnerships with prominent aviation companies such as Boeing, Indigo, and Spicejet, as well as with the three Tata Airlines – Air India, Vistara, and AirAsia India.
This collaboration aims to promote the production of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional aviation fuel.

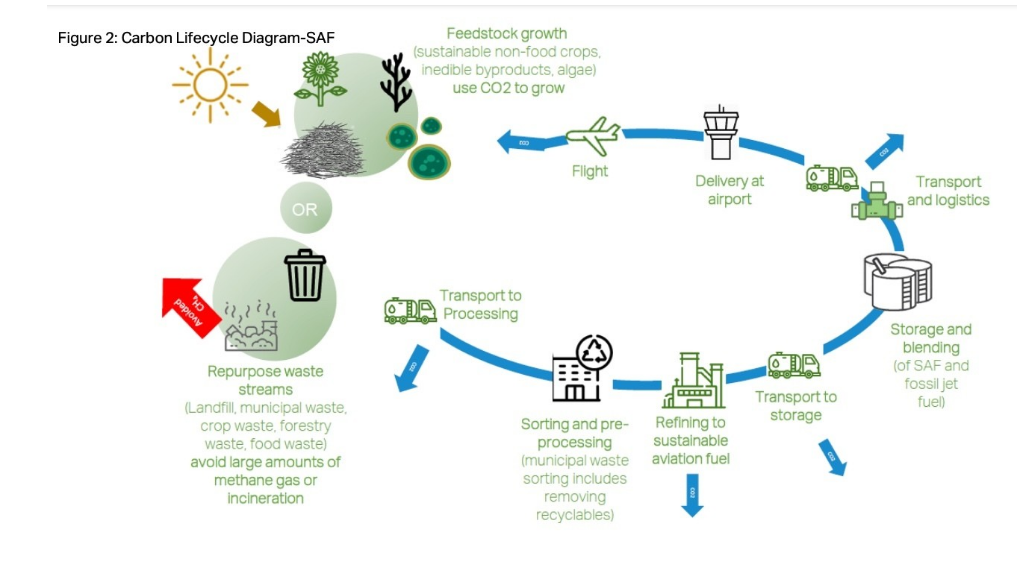
The journey of SAFs commences with feedstock – the raw materials from which these sustainable fuels are derived. Feedstock can encompass virtually any organic matter, including plants, algae, agricultural waste, and even household garbage.
Different Feedstock Sources and Their Characteristics Each feedstock source possesses unique characteristics and challenges. Biomass, which includes crops like corn and sugarcane, is widely employed for SAF production. Algae, while less common, boasts exceptional oil content and efficiency. Waste materials, such as used cooking oil and municipal solid waste, are also being explored as potential feedstock sources.
Importance of Feedstock Selection in SAF Production Selecting the appropriate feedstock is of paramount importance to ensure the sustainability of SAF production. This choice not only impacts the efficiency of the conversion process but also plays a pivotal role in the environmental and economic dimensions of the SAF journey.
Technologies and Processes Involved in Converting Feedstock to SAFs The conversion of feedstock into SAFs entails a range of complex technologies, including hydro processing, Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, and pyrolysis. These processes break down the feedstock into the constituent molecules that make up jet fuel. Advanced refining techniques are employed to ensure that SAFs conform to aviation fuel standards.
The Role of Biofuel Refineries and Production Facilities Biofuel refineries are pivotal in the conversion process. These facilities are tasked with refining raw feedstock into high-quality SAFs. Scaling up biofuel production is a crucial step to meet the burgeoning demand for SAFs.
Ensuring Sustainability and Efficiency in the Conversion Process Efficiency and sustainability are paramount during the conversion process. Innovative techniques, such as carbon capture and utilization, are currently being explored to further reduce emissions and minimize waste in the SAF production process.
A rich array of feedstock options is available for SAF production. The primary categories include biomass, algae, and waste materials, each offering unique advantages and limitations.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Feedstock Source Biomass, with its abundance and well-established infrastructure, does, however, pose challenges related to competition with food crops for land and water resources. Algae stands out for its high efficiency, but it is still in the experimental stage. Waste materials present an environmentally sustainable solution, although the collection and processing of these materials can be logistically complex.
Case Studies of Successful Feedstock Utilization Several success stories within the SAF industry underscore the potential of different feedstock sources. These case studies serve as real-world examples of how SAFs can be produced sustainably and efficiently, contributing to a greener future for aviation.
Challenges facing SAF production include:
In response to these challenges, researchers and industry leaders are actively exploring solutions. Innovations such as genetically modified crops and more efficient conversion processes are on the horizon, offering potential solutions to these hurdles.
Regulations and incentives play a pivotal role in fostering SAF development. Governments worldwide are implementing policies aimed at encouraging the aviation industry to adopt SAFs, thereby creating a favorable environment for their continued development and use.
In the context of aviation and sustainable fuel, it has the potential to bring about a significant transformation by ensuring transparency, traceability, and accountability across the entire supply chain.
Blockchain can establish an unchangeable and easily accessible record of every stage in the creation, distribution, and utilization of sustainable aviation fuel. This enables the verification of the source, quality, and carbon reduction linked to each fuel batch, fostering trust among all involved parties.
Airlines, regulatory authorities, and consumers have the ability to track the entire lifecycle of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), from its origin to its utilization in an aircraft. This guarantees that the fuel’s assertions about sustainability are supported by authenticated data, effectively countering deceptive environmental claims and promoting authentic environmental responsibility.
The smart contract features of blockchain can streamline the process of calculating and conducting carbon credit transactions automatically. Airlines adopting Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) can receive carbon credits as a reward, and these credits can be openly traded on blockchain platforms. This approach offers incentives for transitioning towards more sustainable practices.
Blockchain facilitates the safe exchange of information among various stakeholders in the aviation ecosystem, spanning fuel producers, airlines, regulatory authorities, and travellers. This smooth cooperation has the potential to expedite the worldwide acceptance of sustainable aviation fuel.
TraceX’s blockchain traceability and sustainability platform plays a pivotal role in establishing transparency, accountability, and sustainability in the aviation industry and beyond, making it a valuable tool for those committed to reducing the environmental footprint of their operations.
Growth of the SAF Market and Its Economic Implications The SAF market is experiencing steady growth, with significant investments being channeled into the sector. This growth has not only economic implications but also underscores the industry’s commitment to sustainability.
Collaborations and Investments in SAF Research and Production Airlines, aircraft manufacturers, and fuel suppliers are increasingly forming collaborations and investing in research and production facilities dedicated to SAFs. These partnerships are instrumental in advancing the SAF sector and fostering innovation.
Government Policies and Incentives Promoting SAF Adoption Governments across the globe are introducing a range of incentives, tax breaks, and mandates to encourage the aviation industry to embrace SAFs. These policies create an encouraging environment for the development and adoption of SAFs, contributing to a more sustainable future.
The future of SAFs appears promising, with ongoing research and development efforts expected to yield advancements in technology and availability. These developments are likely to make SAFs more sustainable and cost-effective solutions for the aviation industry.
The EU has established blending targets for SAF to reduce GHG emissions from aviation, starting at 2% in 2025 and aiming for 63% blending by 2050.
The Role of SAFs in Achieving Sustainable Aviation and Global Climate Goals SAFs stand as a critical component in helping the aviation industry achieve its sustainability and climate goals. They offer a practical pathway to reducing carbon emissions and aligning with global climate objectives.
Encouragement for Further Investment and Research in SAFs The feed to fuel journey of SAFs holds immense potential for transforming the aviation industry. Encouraging continued investment and research in SAFs is crucial for realizing a more sustainable future for air travel.
Sustainable aviation fuels transcend being mere alternatives to traditional jet fuels; they represent a pathway to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future for air travel. The journey from feedstock to fuel is intricate, marked by a tapestry of innovation and challenges. As the aviation industry grapples with the imperative to reduce its carbon emissions, SAFs shine as a beacon of hope, providing a tangible and pragmatic solution for greener skies. The sky’s the limit, and SAFs are propelling us toward it sustainably. The “feed to fuel” story is not merely a concept; it’s a narrative of transformation, illustrating the aviation industry’s commitment to a sustainable future.
