Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Dive into the fascinating world of poultry! This blog explores the journey of your chicken nugget, from farm to fork. Learn about the complex poultry value chain, the actors involved, and the challenges they face. Discover how technology like blockchain is revolutionizing traceability and ensuring ethical sourcing. Get clued-in on how your choices can impact the future of poultry production!
Have you ever wondered how your delicious chicken gets from farm to fork? This fascinating journey involves a complex network of activities and actors – the poultry value chain.
Fuelled by its affordability, nutritional value, and ease of preparation, global poultry consumption is on the rise, projected to reach over 140 million metric tons by 2025.
Just like any product we consume, understanding its value chain sheds light on its story. It’s a roadmap that reveals the intricate steps involved in bringing poultry to our tables. It’s not just about raising chickens; it’s a multi-layered system encompassing breeding, feed production, processing, distribution, and finally, reaching consumers.
India is currently the third largest egg producer in the world as per the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 2016 and the fifth largest producer of broiler production. India currently processes only 6% of poultry and 21% of meat.
According to the IMARC Group, the Indian poultry market reached a value of INR 1988. billion in 2020 and it expects the market to grow at a CAGR of 15.2% during 2021-26. The production of eggs and broilers has been rising at a rate of 8 to 10% per annum.
Poultry companies occupy a crucial position in the supply chain, collaborating closely with farmers and upstream suppliers, while also maintaining relationships with retailers and grocers. Additionally, numerous poultry companies have direct consumer interactions, boasting recognized brands and products.
The journey of a chicken nugget or a perfectly cooked egg starts long before it lands on your plate.
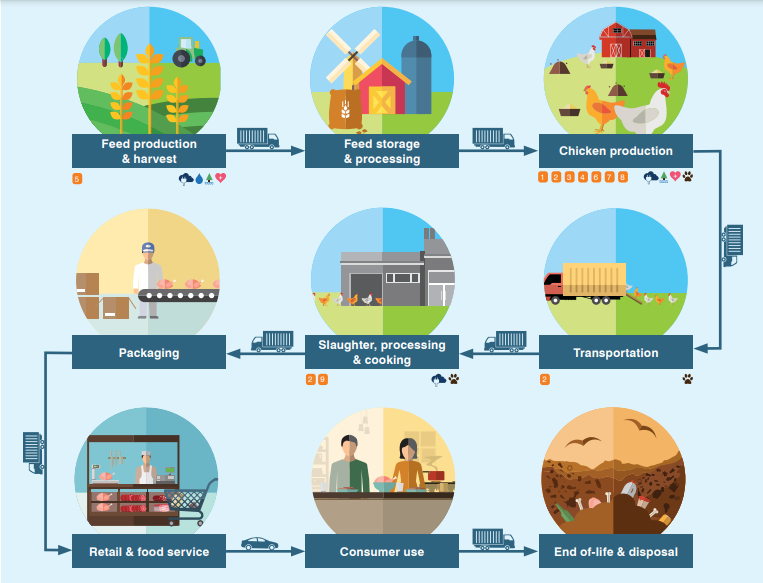
1. Breeding Stock:
It all begins with specialized breeding farms. These farms are responsible for producing high-quality parent stock – breeding chickens specifically chosen for desirable traits like rapid growth rate in broilers (meat chickens) or high egg production in layers (egg-laying hens). Breeding programs involve strict selection processes and genetic management to ensure offspring inherit these valuable characteristics.
2. Hatcheries:
The magic of life unfolds in hatcheries. Here, fertilized eggs from breeding stock are carefully incubated under controlled temperature and humidity conditions. Advanced technology monitors the development of the chicks, and after a specific incubation period (typically 21 days for chickens), healthy chicks hatch and are prepared for transport to poultry farms.
3. Feed Production:
Poultry thrives on a balanced and nutritious diet. Feed mills play a crucial role in the value chain by producing formulated feed specifically designed for different poultry life stages (starter, grower, finisher for broilers; layer feed for egg production). These feeds contain essential ingredients like grains, protein sources (soybean meal), vitamins, and minerals, ensuring optimal growth, health, and egg production in the birds.
4. Poultry Farming:
This is where the chicks become the stars of the show! Poultry farms come in various models, each with its own management practices:
5. Processing and Slaughtering:
Once broilers reach maturity (typically around 6-7 weeks), they are transported to processing facilities. Strict regulations govern hygiene standards throughout the process. The birds are humanely slaughtered, defeathered, and eviscerated. Initial processing involves cleaning, chilling, and portioning the chicken into various cuts or preparing them for further processing into products like nuggets or sausages. Eggs are also carefully sorted, cleaned, graded, and packaged for distribution.
6. Distribution and Logistics:
Maintaining freshness and safety is paramount. Poultry products are highly perishable and require efficient cold chain logistics. Refrigerated trucks and temperature-controlled warehouses ensure the products reach retailers and consumers in optimal condition.
7. Retail and Consumers:
Finally, the journey ends at grocery stores, butcher shops, wet markets, or even online retailers. Consumers have a wide variety of choices, from whole chickens and fresh eggs to pre-cut parts and marinated options. Purchasing decisions are influenced by factors like price, convenience, and growing ethical considerations around animal welfare and sustainable farming practices.
This comprehensive view of the poultry value chain highlights the collaborative effort of numerous actors, each playing a vital role in getting poultry from farm to fork. Understanding these stages sheds light on the complex journey of this protein source and the various factors that influence its quality, safety, and affordability for consumers worldwide.
The poultry value chain, while delivering a global protein source, faces a multitude of challenges that can impact efficiency, profitability, and sustainability.
These challenges highlight the interconnectedness of the poultry value chain. Issues at one stage can ripple through the entire system. However, innovation and collaboration are paving the way for solutions. Technological advancements in biosecurity, feed production, and traceability offer opportunities to address some of these hurdles. Furthermore, a focus on sustainable practices throughout the chain can benefit not only the environment but also the long-term viability of the poultry industry.
The need for poultry traceability stems from a multitude of factors impacting consumer trust, food safety, and overall efficiency within the poultry value chain. Here’s a breakdown of the key reasons why traceability is crucial:
Uncover how transparency initiatives are revolutionizing the food industry, ensuring safer products for consumers.
Discover the key to food safety through enhanced supply chain transparency.

In the ever-evolving world of food safety and transparency, technology offers a suite of solutions to enhance poultry traceability throughout the value chain. Here’s a look at some of the most promising advancements:
1. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID):
2. Barcode Technology:
3. Blockchain Technology:
4. Sensor Technology:
5. Internet of Things (IoT):
6. Big Data Analytics:
While each technology offers unique advantages, the most effective approach often involves a combination of these solutions. Integrating RFID with blockchain technology, for example, can create a secure and detailed record of a bird’s journey, while sensor data combined with analytics can help identify potential health concerns before they escalate.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of poultry traceability is bright. By embracing these advancements and fostering collaboration across the value chain, stakeholders can create a more transparent, efficient, and ultimately, a more sustainable poultry industry that delivers safe and ethically sourced protein to consumers worldwide.
TraceX, with its blockchain-powered platform, emerges as a game-changer in poultry traceability. Imagine a secure digital ledger recording every step a chicken takes, from farm origin to your plate. TraceX facilitates this by allowing all stakeholders – breeders, farmers, processors, and retailers – to securely record data like feed source, medication history, and transport conditions. This data is tamper-proof and accessible to authorized users, providing unprecedented transparency throughout the chain. Consumers gain peace of mind knowing exactly where their poultry comes from and how it was raised, while producers can showcase their commitment to ethical practices and biosecurity. TraceX empowers the poultry industry to build trust, ensure food safety, and meet the evolving demands of a transparency-driven marketplace.
The poultry value chain, while delivering a vital protein source, is a complex system facing numerous challenges. However, innovation and collaboration are paving the way for a more sustainable and transparent future. By embracing technological solutions like TraceX’s blockchain platform, the industry can address traceability concerns, build consumer trust, and ensure ethically sourced poultry reaches our plates. As we move forward, prioritizing responsible practices throughout the chain, from breeding stock to consumer choices, will be key to securing a healthy and sustainable poultry sector for generations to come.
