Contact: +91 99725 24322 |
Menu
Menu
Quick summary: Explore the dynamic interplay between Organic and Conventional Farming in the context of Sustainable Food Supply Chains. Uncover the environmental impact, nutritional aspects, and the role each plays in building resilient and eco-friendly agricultural practices. Dive into the complexities of these two approaches to better understand their contributions to a sustainable food future.

In today’s world, where sustainability and environmental impact are at the forefront of our concerns, the debate between organic v/s conventional farming practices has become more significant than ever. Both methods play crucial roles in shaping our food supply chains and influencing the future of agriculture. As consumers and businesses increasingly seek to make informed choices about the food they consume and produce, it is essential to understand the pros and cons of each approach.
According to research from National Academy of Sciences, the actual premiums paid to organic farmers ranged from 29 to 32 percent above conventional prices. Even with organic crop yields as much as 18 percent lower than conventional, the break-even point for organic agriculture was 5 to 7 percent.
In this blog post, we delve into the nuances of organic and conventional farming in the context of sustainable food supply chains. We explore the environmental impact, nutritional value and long-term sustainability of each approach. By shedding light on the strengths and weaknesses of both methods, we aim to provide a understanding of how these practices contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system.
In order to address issues like climate change, food security, and environmental degradation, sustainable food supply chains are crucial. We can build a more resilient, just, and ecologically friendly food system for both the present and future generations by implementing sustainable practices along the entire supply chain, from production to consumption.
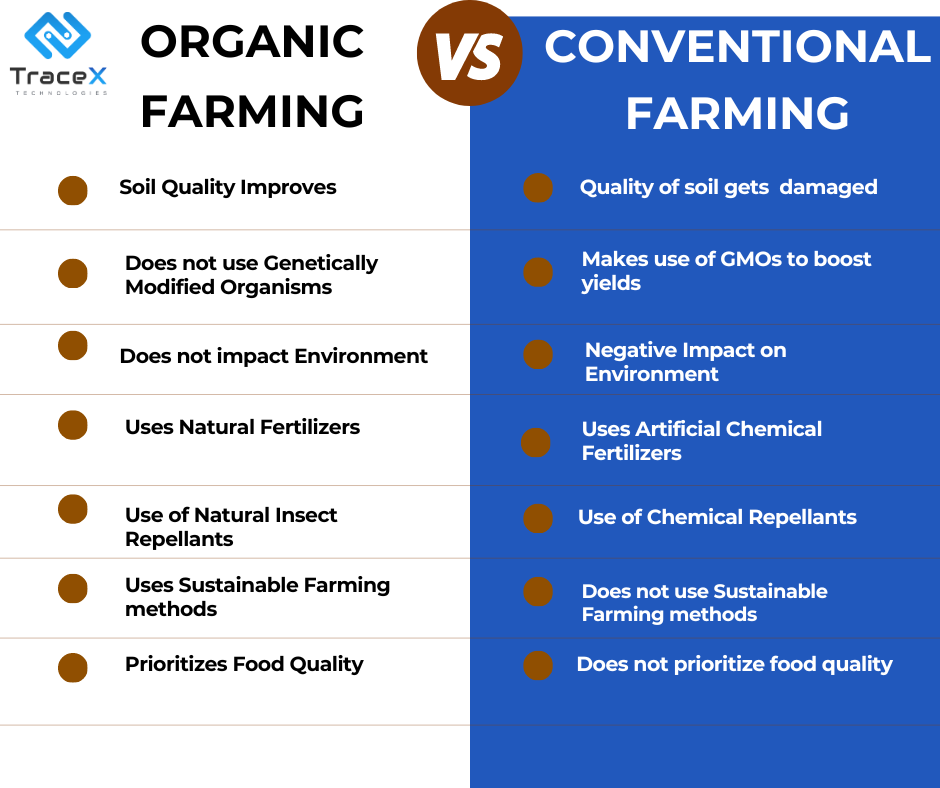
Organic farming with its emphasis on natural methods and minimal use of synthetic inputs, is often perceived as more environmentally friendly and healthier. On the other hand, conventional farming with its reliance on modern technology and conventional pesticides, has been instrumental in increasing food production to meet the demands of a growing population.
When deciding between organic and conventional farming practices, factors like the influence on the environment, human health, animal welfare, and the viability of agricultural systems must be considered. To enhance farming practices, lessen negative effects, and move towards a more sustainable and resilient food system, research and innovation in both directions are crucial.
Organic farming is a method of producing food that prioritizes natural methods while minimizing its negative effects on the environment. Its guiding principles include a dedication to continual improvement, soil health, ecological balance, a ban on synthetic inputs, animal care, traceability, and labeling. The goal of organic farming is to develop a sustainable, all-encompassing system that benefits the soil’s health, biodiversity, animals, and consumers.
There are various environmental advantages to organic farming.
Organic farming is a sustainable and environmentally friendly kind of agriculture because of these benefits to the environment.
The use of pesticides and other chemicals is decreased, which is one of organic farming’s major environmental advantages. Contrary to conventional farming, organic farming prioritizes organic and natural approaches to disease and pest control. Organic farming contributes to reducing chemical pollution in soil, water, and ecosystems by eliminating synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers. By assuring cleaner air, water, and food supplies, this decrease in pesticide and chemical use not only lessens the possibility of harm to wildlife and other beneficial organisms. It also contributes to protecting human health
Conservation of biodiversity and soil health are given top priority in organic farming. Organic farming techniques increase soil fertility, structure, and water retention through the use of organic matter, composting, and crop rotation, promoting long-term productivity and lowering erosion. Additionally, organic farming fosters biodiversity by preserving habitats, utilizing a variety of crops, and using organic pesticides. By fostering a healthier and more resilient ecosystem, these practices protect the natural equilibrium of the environment while fostering the growth of beneficial insects, birds, and wildlife.
In organic farming, certification and labelling standards are crucial. To promote openness and customer confidence, they entail adhering to certification requirements and specified criteria. Consumers may be confident that organic products have been produced using organic agricultural methods since they are labelled to reflect their organic status.
In order to increase crop yields, conventional farming frequently employs synthetic fertilizers, insecticides, herbicides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). In order to increase productivity and efficiency, it frequently uses mechanization. Traditional farming prioritizes high yields and makes use of chemical inputs to manage pests and illnesses. However, it has sparked worries about the effects on the environment, the deterioration of the soil, and potential health hazards brought on by chemical residues.
Using synthetic fertilizers, insecticides, herbicides, and cutting-edge technologies, conventional farming tries to maximize production and yield. These techniques are used in conventional farming to maximize crop yield, boost effectiveness, and satisfy the rising food demand. Conventional farming methods place a lot of emphasis on getting higher yields. It’s crucial to remember that conventional farming’s improved production and yield may have significant negative effects on the environment and human health.
Modern technology is embraced by conventional farming to improve the effectiveness of agricultural practices. It automates processes, boosts output, and requires less labour by using machines, irrigation systems, and cutting-edge technologies. These technical advancements include data-driven decision-making, automated systems, and precision agriculture. Utilizing technology, traditional farming seeks to maximize resource use, reduce waste, and increase efficiency in a number of areas related to crop production and management.
The use of chemicals in conventional farming presents problems and has an influence on the environment. Chemical residues in soil, water, and food may result from the widespread use of synthetic fertilizers, insecticides, and herbicides. This could hurt non-target creatures and have negative consequences on ecosystems such as biodiversity loss, tainted water sources, and injury. Chemical runoffs can disturb aquatic habitats and lead to water pollution. In addition, repeated and excessive chemical use over time may result in soil deterioration, nutritional imbalances, and decreased soil fertility. For the development of more sustainable and ecologically friendly farming practices, addressing these issues is essential.
The benefits of organic farming far surpass those of conventional farming. As previously highlighted, organic farming aims to preserve soil fertility, offer people wholesome and nutritious food, safeguard both environmental and human health, and pave the way for sustainable agricultural practices.
Unlike conventional farming, which primarily emphasizes producing large quantities of food for profit, organic farming prioritizes the holistic well-being of the world. This encompasses humans, animals, insects, plants, soil, water, and air.
TraceX blockchain powered traceability solutions are a comprehensive toolset for the tracking and improvement of organic farming practices. By leveraging technology to enhance transparency, compliance, and efficiency, they empower farmers to embrace and thrive in the realm of organic agriculture. TraceX facilitates the documentation of each stage of organic farming, from seed selection to cultivation methods. It creates a transparent supply chain for organic produce. By tracking the movement of goods from farm to market, consumers can be confident in the authenticity of organic products.
The solutions provide real-time monitoring of farming activities. This includes data on soil health, water usage, and pest control methods. Farmers can make informed decisions based on this data, optimizing their organic practices for better yields while staying true to organic principles. By maintaining accurate records and providing evidence of adherence to organic guidelines, farmers can streamline the certification process and build trust with consumers.
Finding solutions for organic and conventional farming practices to coexist amicably and complementarily within the agricultural environment is a key component of coexistence and integration. Practises such as buffer zones, agricultural diversity, and joint activities can help achieve this. Farmers can select the farming technique that best fits their objectives and available resources through coexistence while lowering the possibility of contamination or conflict.
Moving from conventional to organic farming necessitates a change to more environmentally responsible and sustainable practices. Farmers often start by assessing and enhancing the condition of the soil through techniques like cover crops and composting. They utilize organically approved substitutes for fertilization, pest control, and weed management as they phase out synthetic inputs over time. To improve ecological balance, crop rotation, biodiversity enhancement, and natural pest predators are integrated.
Food that is locally produced and environmentally friendly must be chosen and promoted in order to support local and sustainable agriculture. Purchases from neighbourhood farmers, farmers’ markets, and community-supported agriculture initiatives are encouraged. By doing this, people may promote food security, boost local economies, and lessen the carbon footprint associated with transportation. Supporting sustainable agriculture also entails choosing methods that place a high priority on soil health, biodiversity preservation, and the use of few synthetic inputs.
In conclusion, tackling the environmental, social, and economic issues that our agricultural systems are confronting requires the development of sustainable food supply chains. Contrary to conventional farming, organic farming has significant environmental advantages thanks to its emphasis on natural practices, soil health, biodiversity preservation, and less chemical use. The issue of juggling economic factors with sustainability objectives persists. The cohabitation and integration of farming practices can promote a more diverse and resilient agricultural system. Both organic and conventional farming offer advantages. To encourage healthier ecosystems, preserve natural resources, and guarantee food security for future generations, it is essential to support local and sustainable agriculture.
