Cocoa farming in Ghana
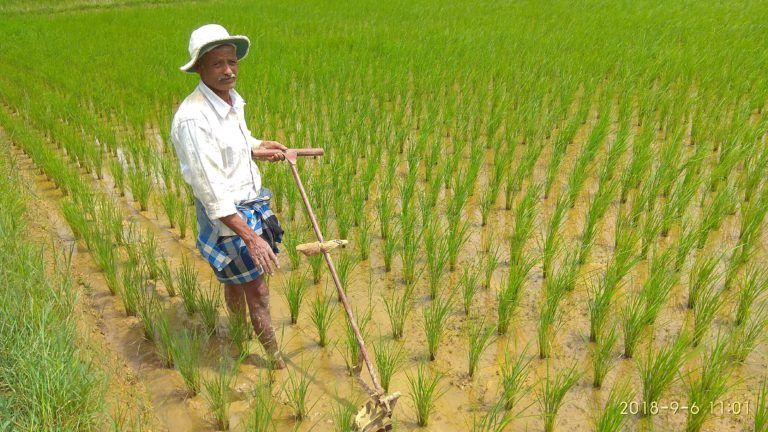
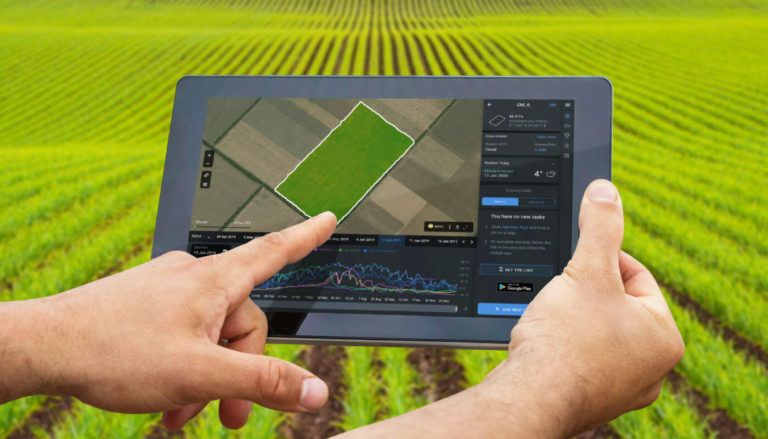
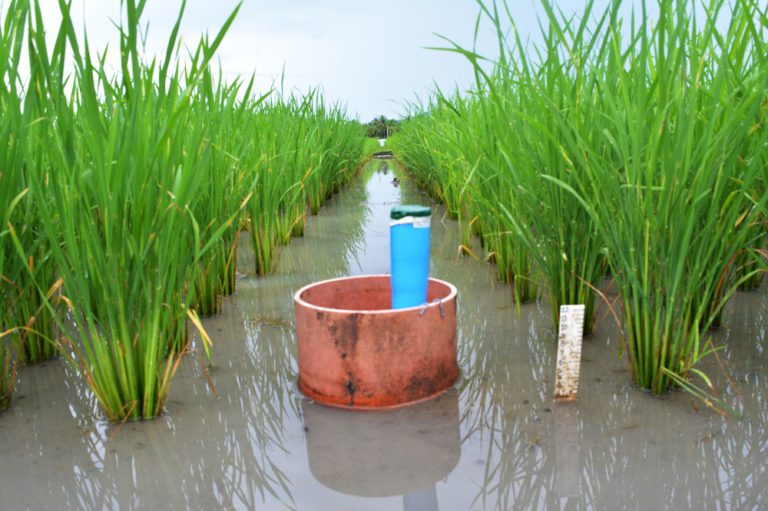
Unlock the secrets of cocoa farming in Ghana! Dive into the rich world of cocoa cultivation in Ghana, where smallholder farmers play a vital role. Explore the challenges they face and the innovative solutions transforming their livelihoods. Join us on a journey through the cocoa fields of Ghana and discover the story behind the world’s favorite indulgence.